What Is That Pain In The Back of My Heel?
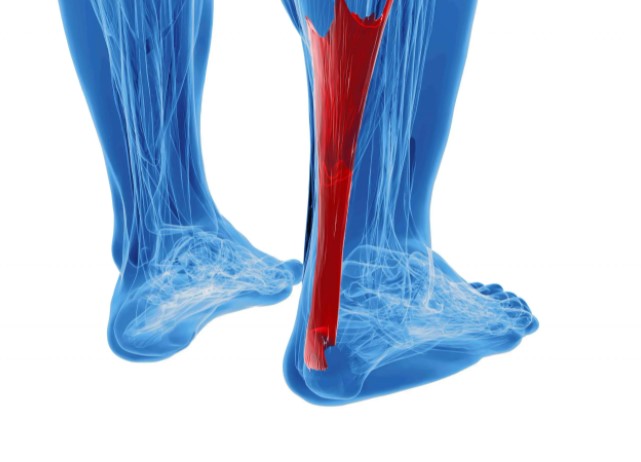
The Achillies tendon is the largest tendon in the body. It is used to walk, run, climb stairs, jump and stand on tip toes.
Achillies tendonitis is inflammation of the Achillies tendon. It can occur within the tendon itself or at the point where it attaches to the heel bone, called the Achillies insertion.
Inflammation is part of the body’s natural response to injury or disease and it presents as swelling, redness and pain. Tendonitis is often seen in people who have excessive pronation or flattening of the arch. It can also occur in people who have weak or tight calf muscles or bone spurring behind the heel. People who are runners or involved in sports, particularly sports that require quick starting and stopping or people who participate in sports less frequently, leaving their bodies less used to stress.
Tendonitis pain will generally resolve with treatment. However, if tendinitis is unresolved, the condition may progress to degenerative changes to the Achillies tendon which is called Achilles tendonosis.
Achillies tendonosis is degeneration of the tendon that may lead to degenerative tears and chronic pain issues. The most common area where degenerative tears are noted is at the insertion into the heel bone. This may be seen in years of over use, people who put an excessive amount of work on their feet at work.
Achillies Tendon rupture is a tear or break in the tendon
Types of Achillies Tendinitis:
Noninsertional Achillies Tendinitis – the middle portion of the tendon is affected. Mostly occurs in younger patients and athletes.
Insertional Achillies Tendinitis – involves the area where the Achillies tendon attaches to the back of the calcaneus. Often seen after years of overuse, but can affect anyone.
Symptoms include pain, aching and stiffness of the Achillies tendon. Often painful when the sides of the tendons are squeezed. Sometimes thickening of the tendon is palpable or visible with visible nodules. Leg weakness and swelling around the tendon may be noted.
Clinical examination involving palpation and range of motion are evaluated to determine the health and strength of the tendon. Imaging studies such as x-ray, ultrasound or MRI can also be used to further asses health and integrity of the tendon.
Treatment consists of RICE, NSAIDS, supportive shoes, heel lifts or custom orthotics. Avoid walking in very flat shoes or barefoot. A night splint can help the Achilles tendon stretch as you sleep and a walking boot may be indicated if the pain is severe. Eccentric exercises at home and physical therapy which includes stretching, strengthening and massage. An additional conservative measure with great success rates is Extracorporeal shockwave therapy. Sound waves are used to promote healing and reduce the symptoms of pain.
If conservative treatments fail, surgical interventions may be indicated. Common surgical therapies include: gastric recession, debridement and repair and debridement with tendon transfer in severe cases.
If you have any questions or concerns please call Quality Foot Care at 215 230-9707 for a comprehensive examination and expert treatment.


Leave A Comment